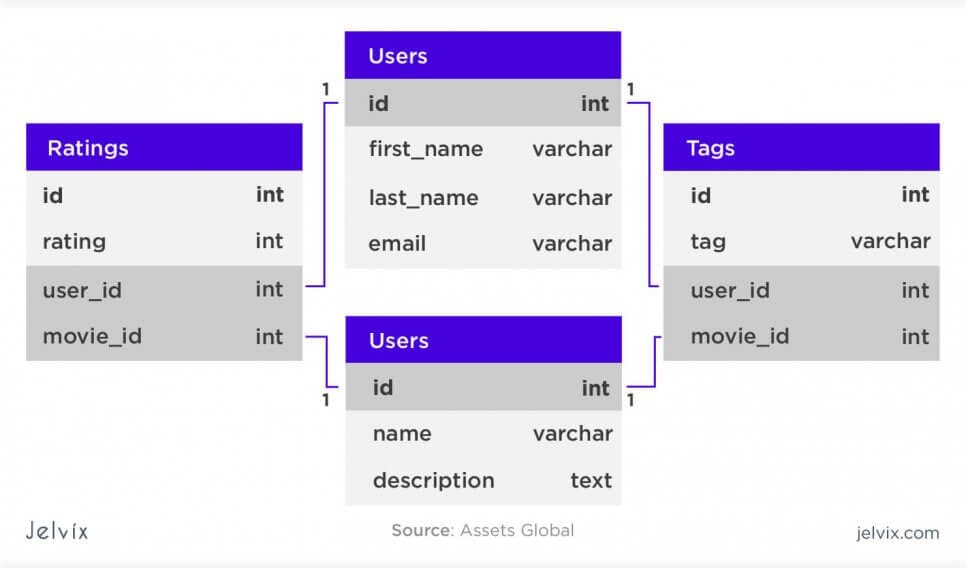
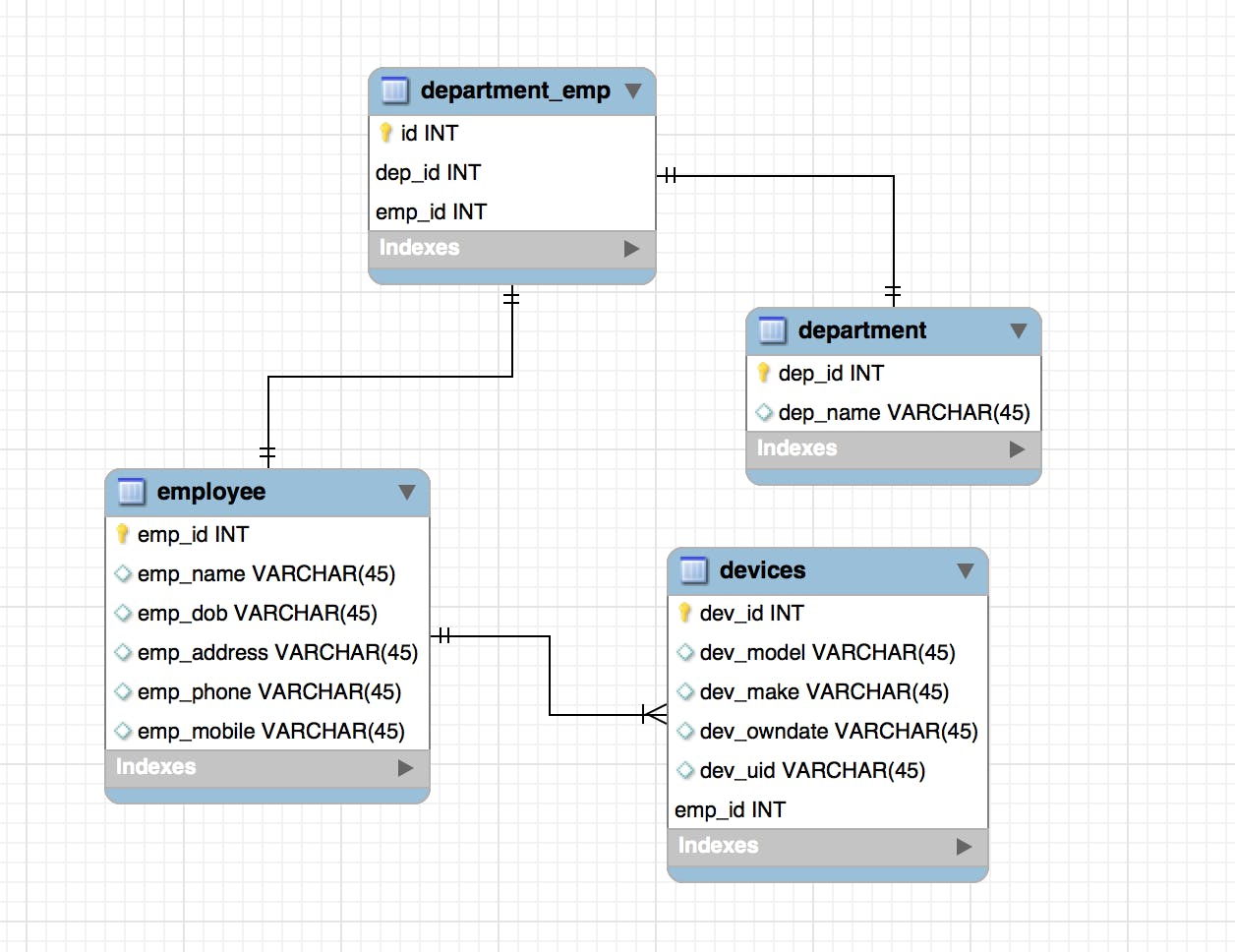
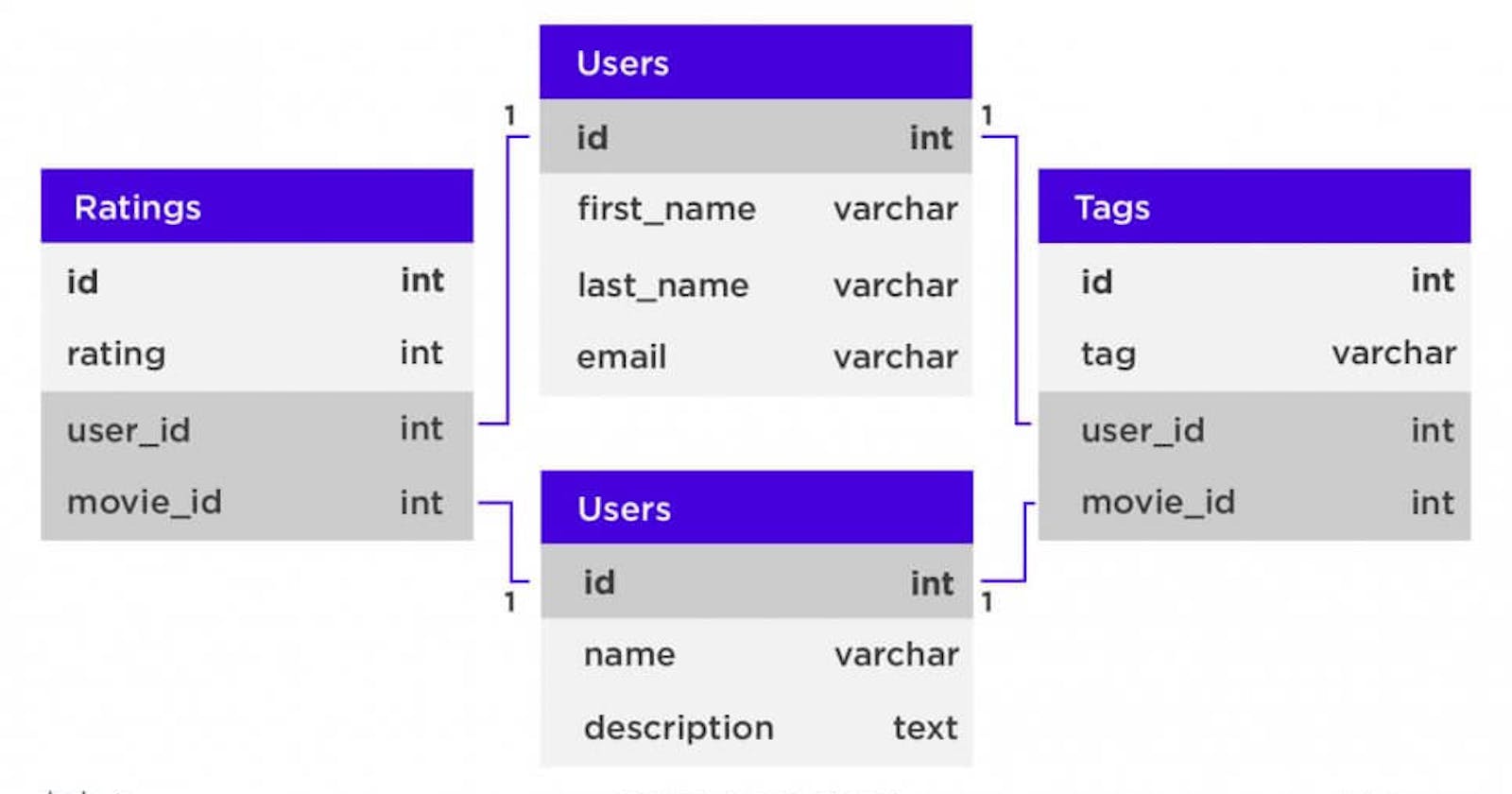
Relational databases store information with columns, rows, and tables, meaning the data is organized in tables. However, the data within these tables have relationships with one another or dependencies. A relational database works by linking information from multiple tables through the use of “keys.” A key is a unique identifier that can be assigned to a row of data contained within a table. This unique identifier called a “primary key,” can then be included in a record located in another table when that record has a relationship to the primary record in the main table. When this unique primary key is added to a record in another table, it is called a “foreign key” in the associated table. The connection between the primary and foreign keys then creates the “relationship” between records contained across multiple tables. Relational databases are also called Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) or SQL(Structured Query Language) databases. SQL is used to execute queries, retrieve data, and edit data by creating, updating, or deleting new records.